INFLUENCE OF A FREE ELEVATOR ON LIFT AND MOMENT
In Sec. 6.3 we have dealt with the pitch stiffness of an airplane the controls of which are fixed in position. Even with a completely rigid structure, which never exists, a manually operated control cannot be regarded as fixed. A human pilot is incapable of supplying an ideal rigid constraint. When irreversible power controls are fitted, however, the stick-fixed condition is closely approximated. A characteristic of interest from the point of view of flying qualities is the stability of the airplane when the elevator is completely free to rotate about its hinge under the influence of the aerodynamic pressures that act upon it. Normally, the stability in the control-free condition is less than with fixed controls. It is desirable that this difference
|
should be small. Since friction is always present in the control system, the free control is never realized in practice either. However, the two ideal conditions, free control and fixed control, represent the possible extremes. When the control is free, then Ghe = 0, so that from (6.5,2)
|
||
|
||
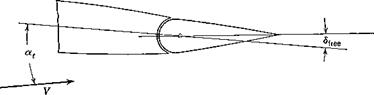
The typical upward deflection of a free-elevator on a tail is shown in Fig. 6.24. The corresponding lift and moment are
![]() Чее = °T^ + °L^e ^“free = ^mS^etree
Чее = °T^ + °L^e ^“free = ^mS^etree
After substituting( 6.6,1) into (6.6,2), we get
C4ree “ % + °L‘* (a)
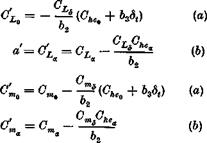 |
When, due consideration is given to the usual signs of the coefficients in these equations, we see that the two important gradients CLa and Cm are reduced in absolute magnitude when the control is released. This leads, broadly speaking, to a reduction of stability.