Low Aspect Ratio Flat Wings
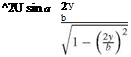 |
|||||
The cross flow over a flat plate is known from Chap. 2, Eq. (2.84), and with the current coordinate system and notation, the velocity components on the plate, in terms of the perturbation potential, are (see Katz and Plotkin [8], Duncan et al. [9])
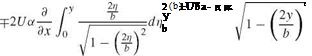 |
||
where b(x) is the wing span, the plus sign is for the lower surface, see Fig.7.10. Since дu/дy = дv/—x, one can find u by integration of дu/дy
From the Bernoulli equation, the pressure jump at a point (x, y, 0) of the wing is given by Ap = p(x, y, 0-) – p(x, y, 0+). This reduces to
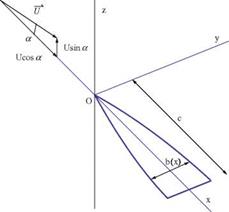 Fig. 7.10 Low aspect ratio flat wing
Fig. 7.10 Low aspect ratio flat wing
![]()
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
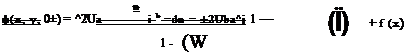 |
|
|

Since ф is an odd function of z and ф is continuous at the wing edge, f (x) = 0. The jump of ф is the circulation f(x, y), hence
|
|
The slender flat wing has elliptic loading. The induced drag is therefore given by the same formula as for a large aspect ratio wing, i. e.
CL nAR 2
CDi = ^ = a2
n AR 4
The induced incidence at is such that CDi = —CLat. One finds at = – a/2. The resulting force due to pressure is not perpendicular to the flat wing, as would be expected, because as in thin airfoil theory, the wing edge experiences a suction force due to the infinite velocity and vacuum pressure at the sharp edge. The force is in the z = 0 plane and its x-component is equal to Fs = —La/2. Note that the suction force does not exist if the leading edge is supersonic.
For triangular wings, the loading is constant along any straight line through the vertex (i. e. conical flow), the angle t with the x-axis being constant along such a line
The pitching moment about the у-axis is given by
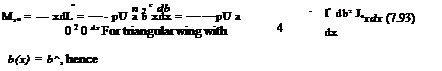 |
|
|
|
![]()
The pitching moment is made dimensionless with the wing area and the chord as
![]() n AR
n AR
Cm, o = 3— a
The center of pressure, as well as the aerodynamic center, for the flat plate wing are found to be located at
![]() (7.96)
(7.96)
Finally, between the body of revolution and the flat wing, one can think of wings with elliptic cross sections. The flat plate cross section is the limiting case of the ellipse.
The order of magnitude for the lift coefficient in this section is consistent with the lifting line theory for elliptic loading of small aspect ratio wings, where CL is proportional to n ARa, and independent of M0.
Following Weissinger [10], the low and high aspect ratio wing formulae are combined in a single expression for extended lifting line theory and after applying the Prandtl/Glauert rule, yielding
^ AR
Ve2 AR2 + 4 + 2











