Longitudinal Force
The longitudinal force is treated in a manner analogous to the lift force. The net forward force is calculated as the forward component of the turned thrust minus the induced and profile drag of the wing. The induced drag is calculated from the sum of CLr=o and CLr and accounts for the deflection of the trailing vortex sheet, according to Fig. 3-9. Because the wing is immersed in the wing slipstream, the profile drag should be calculated relative to this direction.
Referring again to Fig. 8-9, we find that the forward component of the thrust is
X = m[VR cos (as + в) — F],
In dimensionless form
![]() – F
– F
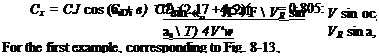 |
|
Again a correction is necessary to account for profile drag losses. Hence C„ becomes
CJnAR. is equal to 0.238, so that from Fig. 3-9 the above equation must be increased by 1.1 or
CDl = 0.88.
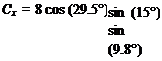 |
||
Cx is thus
= 5.98.
Again these equations are in close agreement with the experiment.











