Algorithmic (Linear Optimal Control) Model
The algorithmic or linear optimal control model is partially a structural pilot model in that elements of the optimal controller can be identified with the neuromuscular lag. However, the basic distinction between the algorithmic and structural pilot models is that, except for simple problems, the pilot cannot be represented with a simple transfer function in the algorithmic case. When very simple airplane dynamics (a pure integrator) are postulated in order to be able to generate a pilot transfer function, the linear optimal control pilot
|
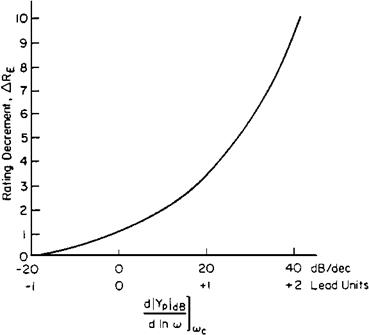
Figure 21.3 Degradations (increases) in pilot rating for tracking tasks associated with degree of pilot lead required. (FromMcRuer, AGARDograph 188, 1974) |
model is found to be of high order, but with characteristics similar to the crossover model (Thompson and McRuer, 1988).
The linear optimal pilot model hasbeen used to advantage in the generation of pilot ratings (Hess, 1976; Anderson and Schmidt, 1987), the analysis of multiaxis problems (McRuer and Schmidt, 1990), and the stability of the pilot-airplane combination in maneuvers (Stengel and Broussard, 1978).