R-4/R-5
• First production helicopter • Successful design • Wartime service
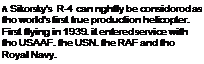
 Many people believe the role of the helicopter in World War II was restricted to experimental flights. The USAAC took it far beyond the test phase and Sikorsky’s diminutive R-4 performed some of the most significant flights of the entire war. Pilots found themselves confronted with an ontiroly now era of flight, and the potential of the military helicopter was quickly seen. As a search and rescuo platform, it was a life-saver.
Many people believe the role of the helicopter in World War II was restricted to experimental flights. The USAAC took it far beyond the test phase and Sikorsky’s diminutive R-4 performed some of the most significant flights of the entire war. Pilots found themselves confronted with an ontiroly now era of flight, and the potential of the military helicopter was quickly seen. As a search and rescuo platform, it was a life-saver.
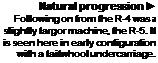
![]()

Workhorse forerunner ►
Although tho R-S was successful.
redesigning it resulted in the S-51. which did more to establish the concept of rotary-winged flight than any other helicopter.
British helicopter evaluation ►
After the R-4 had boon ordered by the US armed sorvicos, a handful found their way overseas. The Royal Air Force and Floot Air Arm evaluated the type during the closing months of World War II. In UK service, they were given tho designation Hoverfly Mk I.
◄ Production gets underway
With flight trials having been conducted successfully, the R-4 was put into production at Stratford. Connecticut in early 1942.
◄ Distinctive looks
Compared to later designs, the R-4 was an ungainly machine featuring a boxed spar fuselage covered in fabric.
FACTS AND FIGURES
>■ On 21 April 1946 я single Canadian R-4 became the lirsl helicopter to rescue n downed crow In the Arctic.
► Thirty production machines (YR-4As and YR-4Bs) wore ordered In total.
>■ US Army Air Forco R-4s wore used to rescue downed crews In the Pacitic.
> By tho time production switched to the Improved R-5/S-51 series, a total of 1Э0 Sikorsky R-4s had been built
>• A Sikorsky R-4 was the tirst truo helicopter to make a landing at sea.
► On 17 May 1042, tho XR-4 new о distance
ot 1224 km {760 ml.).
 |



![]()
![]()
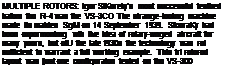

Ідей – Sikorsky finally managed to ll ln> first successful rtMary-wingcd craft in 1939. Known as the N■4-300, it was instrumental in the development ol the world’s :irsi true pnxluction helicopter, the. шы/ing Sikorsky K-1 With the VS-300 (lying at speeds of up to 113 киї h ГО nt. p.h.) by 1941. it was obvious that a more practic-.il machine was viable
Flie resulting XR-J featured an enckxsed cockpit with dual, iide-by-slde seating and a single Warner KStXl piston engine After successful trials, an order for 30 pnxluction aircraft (three YK – l.-Ys and i~ YK-iBsi was placed by the
United States Army Air Force They were laid augmented by Klfi more R-»Bs which featured more powerful engines R – is were pioneers in the development of the helicopter and, on 6 May 1913. an early production machine liecaute the first helicopter lo land successfully aboard a ship, touching down on ilk* aircraft carrier. I SS HtniLxr Hill.
Using the K-i as a Ixtsis. Sikorsky develop’d tlie laiger It-5. which featured an all-metal fuselage and other improvements li first flew in 1943, but did not enter service until after World War II Nevertheless, it proved iremendousJv successful and
some 3"9 of these aircraft, later called S-51. were liuilt.
Al R-4s were tiled with (tveo tiUXwl miwi rotors To reduce wogifl. ttvjy worn connoucttxl from spruce wood, whch proved а problem aunng rescue орогс&опб a Itm P. vcilc. Ihonf/o
Above: This photograph is unique, shovnng the Sikorsky R-4, R-5 and R-6 together. The evolution ol the helicopter can already be seen.
Loft: Col Frank Gregory, who helped to bring about the R-4, was the first person to land a helicopter on board ship.


![]()
![]()
 |
|||
At її ці time, Ww cocXpl rJ the R-4 was <*»!•> u – tsual for nviny plots тгл icaaf: commander – Я n tho nght-fumd sent It л-is not a dittcuft reach*» to t>y ana piOtn Ad go »ofo in >jsi а tow почте.
![]()
![]()

 Early Sikorsky helicopters
Early Sikorsky helicopters
В SIKORSKY R-6: Installing the R-4’s engine and gearbox in a ‘ • л. much more streamlined fuselage resulted m tho R-6 They w – delivered to the RAF as Hovedty Mk Its
Sikorsky











