Hinge Moment Coefficient
The characteristic of a flapped aerofoil, which is of great importance in stability and control of the aircraft, is the aerodynamic moment about the hinge line, H, shown in Figure 6.10.
Taking moments of elementary pressures p acting on the flap, about the hinge:
trailing edge
H = —
pX dx,
hinge
where:
p = pUk
and:
X = x — (1 — F) c.
Now putting:
X = — (1 — cos 0) — — (1 — cos ф = — ( cos Ф — cos 0)
and k from Equation (6.42), we get the hinge moment as:
H = ~f. 2pU![(“ + ‘0 — C>) ^
Substituting:
H = Ch 2 pU 2(Fc)2
![]()
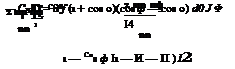 |
||
![]()
![]()
and simplifying, we obtain:
The parameter a1 = dCL/da is 2n and a2 = dCL/dn from Equation (6.43) becomes:
a2 = 2 (n — ф + sin ф). (6.48)
Thus thin aerofoil theory provides an estimate of all the parameters of flapped aerofoil.













