• Largest production helicopter • United Nations relief flights
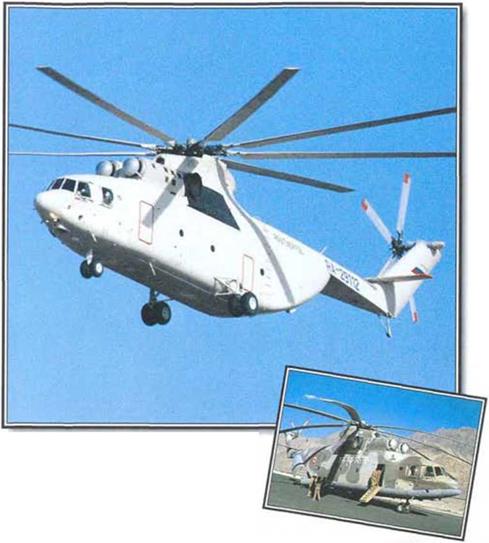
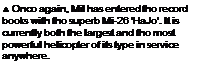 
With tho intention of surpassing the load-carrying capabilities of its mighty Mi-6 ‘Hook1, Mil set about designing its Mi-26 ‘Halo* in the early 1970s. It was clear that the twin-rotor layout of the earlier V-12 had led to a developmental dead end, so Mil set out to produce a thoroughly conventional helicopter on a hugh scale, with a payload up to one and a half times greater than that of any previous rotary-winged type.
 [ [
▼ Enormous capacity
 The presence of thoso troops and a single jeep lend scale to the sue of tho Mr-26. The fuselage is as largo as that of a C-130 Hercules and can accomodate up to 80 fully – equipped soldiers. The presence of thoso troops and a single jeep lend scale to the sue of tho Mr-26. The fuselage is as largo as that of a C-130 Hercules and can accomodate up to 80 fully – equipped soldiers.
  ▼ Special requirement ▼ Special requirement
A primary requirement prompting the design and development of this huge helicopter was for a machine able to carry substantial loads in vast, sparsely- populated areas, such as Sibeha. Tho Mi-26 performs such tasks with ease.
FACTS AND FIGURES
Flown for tho first time In a hover on >• Variants Include the MI-26TZ tanker, wtven
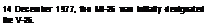 can carry 14040 litres <3.709 gallons) of tue! dispensed on tho ground using 10 hoses can carry 14040 litres <3.709 gallons) of tue! dispensed on tho ground using 10 hoses
>- Machined from titanium, the main-rotor hub is tho largest in the world.
► In the firefighting role, the Mi-26 can drop 7500 litres (2,000 gallons) of fire retardant
>■ External steps and handholds allow
access to the tailboom and rotor.
► A special variant, designated Mi-26MS, w * fully-equipped airborno hospital.
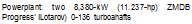 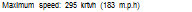 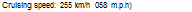  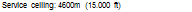 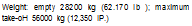 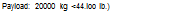  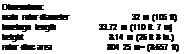  
Using the world’* only
n[KT. uional cighf-hbckxl rotor system, and luving a n’oss-sectkin similar to that of lb’-‘ H-^’T ( ..іікінГ four-turlml. m jirliltfi. the Mi-26 is truly a nuchiiK*«4 4i|vrbtic. v
Vi tilt its eight inlor blades, the Mi-.’" і’ aide i«> ha mile its two 7,i(u.-kV (lo. OOjMip.) turbines, with і rotor ні smaller diamctiT tlun ilutt ol the Mi-6 Power is translerrcd to the rotor shall by a gearlxfX ol unique design It is smallei tlun iIlii of the ‘Hook".
I Hit weighs І.’ЦК) kg I" "20 II» »
Its. strength allows it to control the huge ‘W. OfKLkg tiO. tKHLlh.» maximum torc|iie of the engines A hook beneath the fuselage is stiesstxl for slung loads ol up to
30.0 kg «іб. ООО 111.). Hie principal motivation for the Mi-26 programme was supjxm for exploration work in the remotest areas of Sllkcria. and а Іккік of such capacity is vital if heavy items of equipment are to lx – |xisiiionetl in otherwise iiLueessIble areas. Such Uxations aLso ачцііге the highest levels ol teluhilitv. atul ‘Halos often
Above: When the ‘Halo’ made its debut at Paris in 1981. the French had an apt nickname for it: ‘Le monstre’.
operate under harsh conditions for up to a week without ptoper engineering support As well as its many civilian roles, the Mi-26 is also employed hy the Indian. Russian ami |x>ssibly l kr. iini. ui inilllarv.

|
At first yk»<«. a would appour irvit tlko ‘uta design e very ofcl tueftcred ad arniv to mat of its ptedecesscr. itvo 1960s’ vintage tA-G ’Hoc*’ Mow*». tie read « extremely kgm and compact. and is tre first n Ute wend to carry etf* rotor bodes
|
|
|
Unifco iho mail unit. ti« 1Ы rotor unit was a complete^ now design ixxl kiitirea the composite budus Thr* frt to wfich it is Mted neorperates a tow-tperxi at*o<oi {notion which reduce; load – bearing on the lal гою», ertocfing better stabSy at cnxsing fipeed
|
|
 |
|
fro other heirceter can march the cheer power of the Mfi M’ 26У twin lirbcnrui’l». when enuW* it to Ml «freebie load» In» neared competitor a the I960*’ vntage Swcoky Ch 53E Super Stanoo. which в cowered tiy three enptwe
|
|
|
ni. ji|
supf я smnov
I2M kW
it 0*7 ha
|
|
|
|
|
Mr-» JU10-‘ 16StokW 22 207 be
|
|
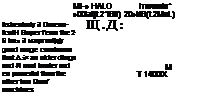 |
|
distmcihe taf – heavy fltance. amtar to tret ot other Ш desgivtd heicootere. To prelect the t/xter&do from damage when the hetcopter is eperatng <i ‘hot-and ingh’ condaons. a heavy-duty tail skd s ffltod
|
|
|
Rear access to the cstvomous fusetago e pruwdod try fftme cbkniBiwiii doom: two hexjo outwwr» and tho thud moerpomies a ‘amp wmen enn be Pwrtred vert саву.
|
|
|
At сгамт. tn* llato’m аЫе to carry the heerrieet payteert though (ho pant ГА-12 hold* the *l-hme record T’w Ot bu£ .» the iMMtf* urge»t heavy-Mt hdccotor
|
|
|
Mil’s milestone helicopters
|
|
|
■ MIL Mi-12 •HOMER’:
Only two oxampies of Ihi*. the largest helicopter ever, were constructed. The Mt – 12 (or V-12) was powered by f our engines; however, technical difficult*» halted development
|
|
|
■ MIL MI-8 HIP’:
Numerically the most | important European helicopter ever built, some 8000 oxamptos have entered service over the years, with а number of operators around the world. Many romaxt m use.
|
|
|
■ MIL M>-1: This little machine has the distinction of bong the first series production Soviet helicopter of conventional configixatioa Now а museumplece. it was a milestone in Russ-ал design.
|
|
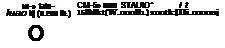 |
   

Mil

irst seen in the WesJ in 197-i, the ‘Hind’ was designed to curry eight men into front-line |XJsition> unit support them with air-to-ground Па – Tlte MI-24 is very large und fast, l»ut it is not us agile. in Wі-stem buulcfield Ikrlicoplcrv However, aircraft like the Aim ж. in ЛІІ-б’І Apache are designed to engage tanks from hklden hovering positions, which calls for low-speed imnt>ouvralnlity. Tlte Hind, by contrast, is a purely offensive
weapon. Ikravlly aimed ami armoured and designed to advance at high speed
Most ‘Hinds’ are gunships. with a stepped tandem canopy housing a weapons oper. dor in front and a pilot (uglier to the tear lather can aim the gun with a magnifying sight in u bulge under tlte nose. which also contains a laser tracker for missiles
After conthut experience in Afghanistan. Mil introduced an improved ‘Hind’ with a twin
MK_____ .A —. ______________ J
Like most Russian weapons the ‘Hind’ is a poworlul machine, built to take battle damage and capablo of operating in very harsh conditions. It will serve for many years yet. as the planned Mi-40 replacement has been cancelled.
barrelled GSlh23L 3d-mm cannon Tills, together with its rockets and missiles, makes the ‘Hind very much a dose – support weapon, with enormous firepower
|
|
|
Mary Hods’ novo an oSro-wd jammer Mtoo to counter vxx*3or oiocnod heetaeekoq miscMs such os Stoger and SA U
|
|
|
This Mi-24 ‘Hmd-E’ serves with the Polish air force-. 56th squadron at InoWroclaw, armed with tho ihturm’ AT-6 lasor-guided anti-tank missile.
|
|
|
Af Ш newoptooi neve а cockwee rotatng rotor The rotor nead лаз buB to withstand heavy rrochme-gun tre
|
|
|
The ‘vaov r..mosnnns aw p^vwn*i годом but they are goting ad may bo ‘otilicoa by ongros u»d о V. -1 Iusku can find lh* money tr> upgado >1» Hods
|
|
|
Large едгаші suppressor» am fitted to some Hods’ to •«**» oka-red signature
|
|
 |
|
■ Me DONNELL DOUGLAS AH-64 APACHE: Much more manoeuvrable at low speeds than the ‘Hind’, the Apache is the West’s premier gunship and anti-tank helicopter. Lrke the txg Mil design. « Is heavily armed and armoured

|
|

|
|
|
Type: battlefield heficoptry
Powerplant: two 1840-kW (t 500-hp.) Khmov (tsotov) TV3-117 Senes III turboshatts
Maximum speed: SlOknVh (192 m p. h.)
|
|
|
ЗоПі cockpits hove виееЯвти ameu protection arm sr-i. s
canopies
|
|
|
the stub wngs snow the Hmd to have very fastUyaddng to tneim from the rotor but C7V
|
|
|
Max cruising speed: 260 km/h (I6i m p h.)
|
|
|
Range: 750 km (465 mi.) with internal luet
|
|
|
Service ceiling: 4500 m (14.760 ft)
|
|
|
Weights: empty 8400 kg (18.400 lb ), loaded 12500 kg (27.500 to )
|
|
|
Armament: one four-barmi jakB 12.7-mm Gatting gun m chm turret; (our S-8 60-mm rocket pods or up to 3460 kg (7.612 lb.) ot rockets or missiles
|
|
|
Dimensions:
span
main rotor diameter
length
herght
|
|
|
6.54 m <2t ft.) 17.3 m (57 ft.) 19 79 m (65 ft) 6.5 m <21 ft.)
|
|
|
Tho fwo-badOd men rotor may bo replaced by that ol (he mom modem Mi-28 Начос’. S the ‘Und’ upgrade programme goto ahead.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Гов ongruk Mnd A’ had 49 tat rotor on ft hi otwtxxtfd s*3e o< the tar boom, but tt was switched to ood soon affix productcn had started.
|
|
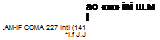 |
|
|
|
|
|
Sper. iaiv prenarm Илов’ «Ubtonod a nsntmr t* hakeem* цдам records in the 7970*. and th* production want remain* on# of th# f**ii*t! паморвег* currtnVf m i«>vc# An «■aonmentnl vo*von ot Briura* Lynn hat vnc# taken th# JCnokit* hotcootw itecO record
|
|
|
|
|
Tho tat rotor romans one ot the waok conts ot the Hhd’ Th* yellow waning зо® hoe tho Russan word for danger oontod on it. a* ground Crews often to* to spot ft when 4 в towng
|
|
|
MI-240 НИЮ 0 ЇМ kaftOQ *1.|
|
|
|
AK-1F COMA
200 In (124 ml.)
|
|
|
НИХ АИ. ІМ 7
270 km |1C7 ml.)
|
|
|
rtns itpiwi eftm *r»t to } Vrr.’, i/xivy cn thn titxnrn lark of hsn mill cneed r»»wy Lvw» to
,’&V’ ftwriw. n thn ЛУ}тг vnr
|
|
|
Th* Mi 24 ■ a twg *rv1 heavy martin# and with * lull corrHMt «Md <i range it noticeably shorter Oran thoaa of it* malt although It can dOuOt# it rang# by carrying drop-tank* n place of naoocray Smc* lb# Unrf і* pnmnrJy а йаЮИаІИ weapon, at tact ot ‘ante i* no real hanocjo
|
|
|
|
|
■ MIL Ml-28 HAVOC’: Even mote powerful than the Hind th*i ‘Havoc’ dispenses with the earlier helicopter‘s раззепдвг cabin И та actively marketed by tho Mil design bureau, but might not nntor service with th* finnnciaSy-stralned Russian military
|
|
|
Ml-240 TONO-O’ AM-1F COBRA LYNX AM Mk 7
4 I AY-2 Snattrt аг 11 TOW niulln «■ TOW «Ittllct AT-6 S?»»r mhsian
Although tha Mind cam** lowo» anv tank wnapont than its rrvalt, it should be namemborad that « waa not d#*gned at an anti-tank platform its ttub wings con be uM to carry a much heevtor vwvghl of other wnapont nctudno bon*». rockets, Oun* and avert chemical woaporit
|
|
 
Mil
• Gunshlp • Tank-buster • Afghan war veteran
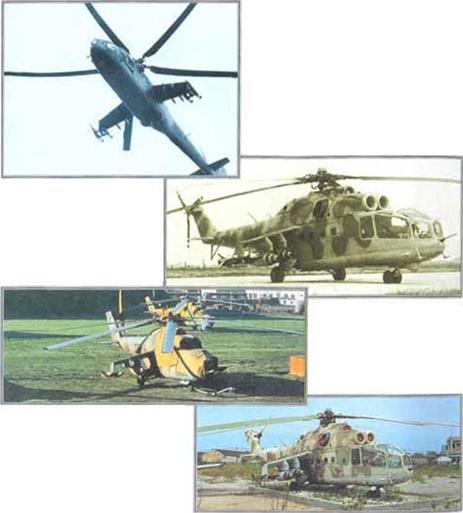
  Tho Mil Mi-24 ‘Hind’ is the hammor of the Russian army. A veteran of battles in Afghanistan and Angola, and most recently in Chechnya, the Mi-24 is a flying armoured personnel carrier, able to deliver a squad of soldiers and cover them with suppressive fire. Armed with a cannon and powerful laser-guided anti-armour missiles, and now fitted with the latest avionics and new engines, the ‘Hind’ is a highly potont attack helicopter. Tho Mil Mi-24 ‘Hind’ is the hammor of the Russian army. A veteran of battles in Afghanistan and Angola, and most recently in Chechnya, the Mi-24 is a flying armoured personnel carrier, able to deliver a squad of soldiers and cover them with suppressive fire. Armed with a cannon and powerful laser-guided anti-armour missiles, and now fitted with the latest avionics and new engines, the ‘Hind’ is a highly potont attack helicopter.
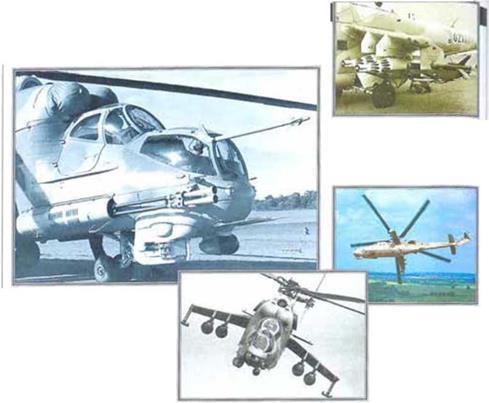
 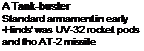 
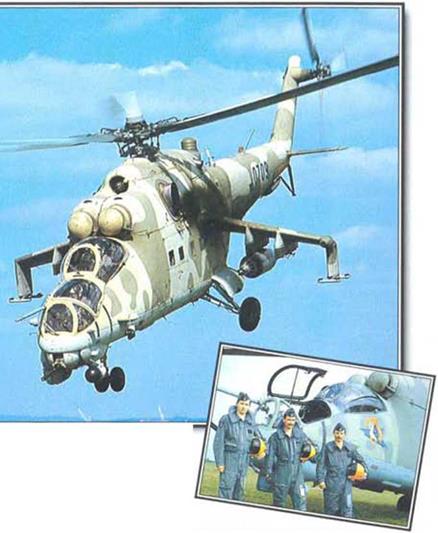
A Twin cannon
The ‘Hmd-F’ replaced the nose turret machine-gun with a fixed twin-barrel 30-mm GSh cannon.
Battle wagon ►
The •Hind‘ proved its toughness in Afghanistan, where it often survtvod massive small-arms tiro.
-4 Guntighter
The ‘Hind-D’ carries tho classic Mi-24 armament fit. A
12.7- mm multibarrel gun turret sharos the nose with an electro – optical guidance system to starboard and a missilo guidance pod to port.
A German ‘Hind’
The Luftwaffe has disposed of its Mi-24 fleet, acquired along with East Germany, mainly duo to poor supplies of spares.
A Fast mover
The ‘Hind’ usod its speed to advantage in attacks, acting much like a ground-attack ict fighter.
FACTS AND
► Tho prototypo Гог tho Mi-24 яогіоя, flttod with a conventional cockpit, made its first flight in 1970.
>> An Mi-24 sot a helicopter world speed record of 368.4 km/h (229 m. p.h.).
► Mt-24s fought against South African troops during tho Angolan war.
FIGURES
► Mujahidoen guorrillas In Afghanistan shot down throe Ml-24s at Jalalabad air base in five minutes using Stinger missiles.
> The ‘Hind’ is oporated by more than two
dozen countries.
>■ Two Mi-24s wore flown to Pakistan by defecting Afghan air forco pilots.
uilt to take tn tops to the – thick of Ixiulcficki action, the MI-2’1 galmxl from Ic*.- n Іі.*апкч1 by IN forces in Vietnam Big enough to carry right troops, it was powerful ami last, and саггіечі enough WCJ|X»ns to suppress Itosttle force– en route to the landing zone – a Hying amtoured personnel carrier.
Mil used ihe TV2-1 Г engines uiu! dynamic system from the Mi « Hip so that design work could coraxturate on the wcai* *ns Installation Ал a result.
the llind-Л was in service witll tin: Soviet fiKccs in |йы Germany from 1973
The IV2-I1“ engines were replaced hy TV 3-І17s m later production aircraft, and the same powcrplant was fitted to some earlier machines llind-As with the later engine have the tail rotor repositioned on the tell of the tail bourn.
I hough the Hind-Л was not exported as widely as some of the later gunship versions of the Mi-24, small numlx-rs have served with the forces of
Afghanistan (where the type saw its first action, mainly in the counter-insurgency role),
Algeria. Lilvya and Vietnam.
The "Hind-C (Mi-2-ІI’ I was a dedicated trjirung version ol the Hincl-A’ with dual оопіпуК Init strip|ycd «if armament. It was one ol these aircraft (designated Л ИП lliat was used in 1973 ю sel eight world marks, including a itumlxT ol sjx44l records, with a female aircrew Front the mid I9"0>. tlu – redc-signc4l Hind i) replaced the A model on the production line.
     td m Ы pUV. r giving, the cockpit of the had throe ranis The crew сопел! nd of * yanuxs n the centre tart я ftght fco pilot befxnd hen to the nw. end the let to the left rear, next to the co-priot In я rose a 12 7 mm І ЬО-cal I macrene – i luted in a tVmtXo mounting td m Ы pUV. r giving, the cockpit of the had throe ranis The crew сопел! nd of * yanuxs n the centre tart я ftght fco pilot befxnd hen to the nw. end the let to the left rear, next to the co-priot In я rose a 12 7 mm І ЬО-cal I macrene – i luted in a tVmtXo mounting
‘Hinds’ at home and abroad
|
■ Mi-240 HINO-O’: The Hlnd-D* was л major redesign ot the Mi-24 intondod to address the weaknesses of tho Huxt-A’ Earty production examples of the new aircraft were duWoftxi to Warsaw Pact countnes. including East Germany

|
|
|
■ f. ti-24 – HIND-A’: Atgenan ‘Hind-As’ served alongsde Mi-4s ana M -3s In 1996 the North African state continued to fly ■Mina though whether these were ‘Hind-As1 is unclear. Few «роп c. ntomers ordered the vanant ___________________________________________________________

|
|
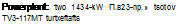 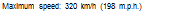 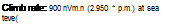 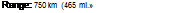 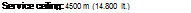 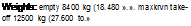  Armament: one 12.7-mm machine-gun and lour AT-2 ‘Swatter’ anti-tank maples plus bombs or two rocket pods Armament: one 12.7-mm machine-gun and lour AT-2 ‘Swatter’ anti-tank maples plus bombs or two rocket pods
Straight wings wittiout anhcdrai identity this Mi-24 as a ‘Hmd-B’ from the first production series.
 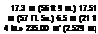 Mi-24 ‘Hind-A’ Mi-24 ‘Hind-A’
|
Libya was among lour Soviet allies to recerve the ‘Hlnd-A’. the others being Algeria. Afghanistan and Viotnam. It is believed that few, If any, ‘Hind-As’ remain in service.
|
|
|
Wl>Je earl/ production Mki As and some lalor Mnd-Ds’ had 1he< taf rotors locator! on the starboard ode of the tar fin, «к»© on що Hmd-As’ worn switched to the pert «*»
|
|
|
Each stub wng can carry two Гatmgn anti-tar* nesstas (krtwn to NATO as AT-2 Swartrus’» as we* as Чи/ 32-round rocker poos Vhnou» antnrwts on trvi aircraft wnie nssocnlefl wth чию equemnnt ora dolertwvo avionics two IFF fldMtfcHon fnand or to*
|
|
|
|
|
|

■ Mi-24P HIND-F: Experience in Afghan-stan led to the replacement of the 12.7-mm nose-moisted machme-gun with a twin-barretlod 30-mm cannon on the МІ-24Р. The Soviot Union and GOR used thts variant, the Mi-35P was an export derivative
A* the Mnd’ nn Oei«k*wl mth new ongne*. • ivOeugr+4 fusettg* eno mom слр*Ы* weapon». и» top spood tuetuisad The w M-?40a war* rrwgnaih «lower than the Tind-A. but by Vm tirrw that the »*-74P Xnd F rod appeared n aarvoi tr*s had bean addrauad. the type hawo a tmaA top «peed margn 0«*r me Ml 240 нт-а
Mi-74 ИШ0-*
Mi-24* ‘WHB-D )10 UMl |1*2 n. p.».)
 X» k«t (201 ■#.*.) X» k«t (201 ■#.*.)
Mil
• Soviet gunship/assault helicopter • Exported • Afghan action
Soviet helicopter pioneer Mikhail Mil’s last helicopter design, the Mi-24, has been ono of the most widely used military helicopters. Tho original Mi-24 prototypo flow in 1970, and was used with two other prototypos to establish several speed, height and climb records. Initial production aircraft wore given tho NATO reporting name •Hind-A’, and were operated by a threo-man crew, including a flight engineer as well as a co-pilot/gunner.
A Well armed
A variety ot weapons (anti-tank missilos, rockets and bombsI were carried on "wings’ attached behind tho cabin. Each had a 250-kg (550-lb.) capacity. Tho Mi-24 saw Its first action in Afghanistan.
A Inspired by HueyCobra
Mikhail Mil studied the American Belt 209 HueyCobra before proposing the Mi-24. The ‘Hind differed from the Cobra In having a troop carrying capability
► Iraqi Mi-249 wore crodited with downing Iranian Cobnt helicopters and ovon F-4 lighter-bombers during tho Iran-Iraq War.
► An Mi-24 prototype new for tho flrst time In early 1970.
► A Hlnd-Л’ was modified to tost syotoms for the lator *Hlnd-D‘.
Pro-production Mi-249 were known as ‘Hind-8’ In tho Wont as they wore not Identified until after production ‘Hind-A*
During the conflict In Afghanistan, MI-24* wore flown by Soviet and Afghan forces
As woll as carrying weapons, tho stub wings provide some lift
• Twin rotor • Heavylift helicopter • Unbroken records
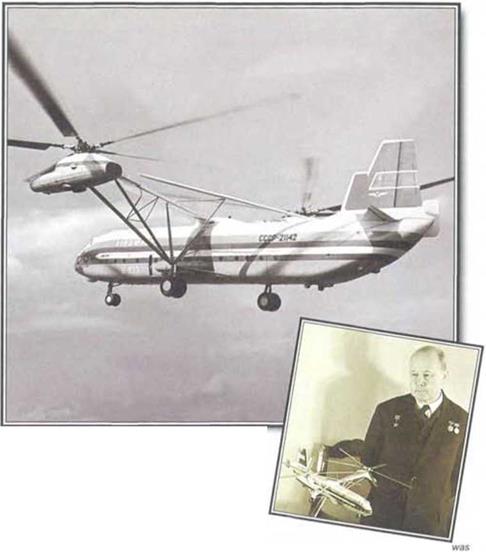  Everything about the V-12 was enormous. The twin-rotor giant shattered every record for helicopter payload, and mado every previous rotarywing machine seem like a toy. But the problems of operating such a machine were also enormous and, despito the Ingenuity of the design, it was not roally a viablo machine for commercial use. After a momorable appearance at the Paris Air Show, the V-12 rarely flew again. Everything about the V-12 was enormous. The twin-rotor giant shattered every record for helicopter payload, and mado every previous rotarywing machine seem like a toy. But the problems of operating such a machine were also enormous and, despito the Ingenuity of the design, it was not roally a viablo machine for commercial use. After a momorable appearance at the Paris Air Show, the V-12 rarely flew again.
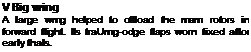 
A Loading ramp
Practical touches like tho rear clamshell doors and loading ramp showed that the V – 12 was not just a record breaker. Tho fuselage intenor also had four cargo winches and a reinforced floor structure.
 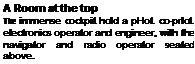 ▼ Paris performance ▼ Paris performance
The Pans Air Show was the V – 12’s greatest moment, attracting enormous attention. But there was little interest in tho machine from foreign customers.
FACTS AND FIGURES
► Tho enormous D-2S turboshaft engines were also used In other very large Mil hollcoptors like the Ml-6 and Mi-10.
► Tho one remaining V-12 con be soon at the Monino air force museum In Moscow.
► Tho V-12 had hydraulic flight controls, but It could also be flown manually.
► Fully loaded, tho V-12 was os hoavy as nlno Mi-24 •Hind’ gunships, or more than twico as hoavy os an MI-6.
>• Tho main cabin of tho V-12 was 28.1 S n’ (83 ft.) long ond 4.4 m (47 ft.) square.
> Optional forry tanks could be carried inside the V-12 for maximum range.
Produced by the man who had built the world s previous largest helicopter. Mikhail Leontyevich Mil the 12 was a giant W ith л mavitmtin lake-oil weight nt over 100 tonnes, it Was biggei than manv transport. lircrati Dcvelo|Hxl with the engines. tnulMmvsion and rotors of the Mi-ti. but in double |K)d> outlv. uil of a long reverse-taper wing, the -li lud a huge fuselage space that contained one-tonne cargo hoists ami seats could ІЧ’ lined for more-
than too passengers The V-I2 even had a split-level flight deck, with pilots and flight engineer lxdow and navigator and radio operator alxive The lust V-12 was damaged in a crash in І‘ХГ. mused by resoiunce and control system problems. Ihe second appeared at the I’ans ir Show and went on to break nutty helico|Mor payload атоїхк. most of which (vmain to this day But despite its stunning performance and size, the V-12 was not really economical to use*, and Mil
Above: Twin-rotor power was a new concept for the Mil company. Despite overcoming many of the technical difficulties, the V-12 was plagued by problems with resonance.
decided to develop the Mi-26 lor heavy cargo Work instead, leaving tlx – V-12 in a museum,
Below: The Soviet obsession with having the biggest and fastest of everything was manifest in the V-12. Mil turned his attentions to the more successful Mi-26 after the problems with the V-12 became apparent.
 |
 |
|
The podded engines tv»d access panels on that undersides lo afVw easy rmntenance. The whole engine asserrety was moulted at a 4′ nose down angle Fuel was carted n the outer wrig section,
|
|
|
The втре centra ftUfm gave me V 12 some rmeh needed stacalty m toward fight suoptomenlod by auOtory tatfns outbowtJ,
|
|
|
Tho pwi Itew the V-12 with the ad of an m/crv’.i! Htsabon system. A ground-mappnq radar лід-. fitted under tho nose
/-Т
|
|
|
V-12 CH S» Mi-26 HALO
ttOOSig ISS. OOO П І 16330 kg (35.326 Ik.) 20000 kg 1*4,000 h I
|
|
|
|
Ueng tour engmea trот the Ш4. the V-12 had nrnxra power The modern M. 20 has ahnosl the same poem trom two more modem enpnet. winch dnvo through a leas waste IU ttarvsnxtaen The СН-5ЭС la dr hen by three rntolrvaly small angne*
 The V-12 had а тпжигмп UAe-oft woght tX 105 torrw*. or mom than a MadM VUcim Bens** The CM-53 s dnirlod try №• much lug» The V-12 had а тпжигмп UAe-oft woght tX 105 torrw*. or mom than a MadM VUcim Bens** The CM-53 s dnirlod try №• much lug»
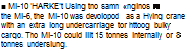      >.U httec&Ti, Out a an почти таеЫ-е. the M.-2S л emost as heavy as a My loaded С-1 Э0 Horses* at та»rm»n oi-up weghc. >.U httec&Ti, Out a an почти таеЫ-е. the M.-2S л emost as heavy as a My loaded С-1 Э0 Horses* at та»rm»n oi-up weghc.
M. 26 HALO
«•53f 56000 kg (123,453 0) )
13400 kg (73.414 lb.)
Mil
• Twin-engined shore-based ASW/SAR helicopter • Exports
  Based on the Mi-8 ‘Hip’, the Mi-14 was developed as a land-based anti-submarine helicopter in the oarly-1970s. A boat hull and retractable landing gear were used to mako it suitable for amphibious operations, with more powerful engines compensating for tho additional weight. Flight tests started in September 1969. Specialised versions for minesweeping and search and rescue operations have also been produced. Based on the Mi-8 ‘Hip’, the Mi-14 was developed as a land-based anti-submarine helicopter in the oarly-1970s. A boat hull and retractable landing gear were used to mako it suitable for amphibious operations, with more powerful engines compensating for tho additional weight. Flight tests started in September 1969. Specialised versions for minesweeping and search and rescue operations have also been produced.
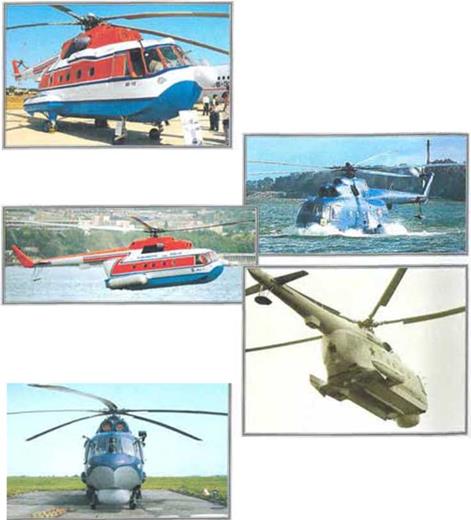
 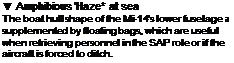 
▼ Upgraded Mi-14 demonstrator
To ‘drum up’ business, tho Russian aviation industry is offering upgrades for existing airframes.
▼ Land based
As featured on other maritime helicopters like the Sikorsky Sea King, the Mi-14 has a shaped hull to provide an amphibious capability.
A ‘Haze’ underside
This view of an Mi – 14’s underside shows the large weapons bay doors open and the MAD ’bird" deployed. Other apertures in tho rear of the fuselage house dipping sonar and include parachutes for sonobuoys and flares.
► Tho Mi-14PL ‘Haze-A’ ontored service In 1976, tho МІ-14ВТ ‘Haze-B’ followed In 1986 and the MI-14PS •Hazo-C’ In 1992.
► Poland was the only export customer for tho search-and-rescue MI-14PS.
► East Gorman Mi-14s were retired after tho German reunification.
The engino and gearbox from tho Mi-17, itsolf developed from the Mi-8, was installed in the Mi-14.
► Tho SAB ‘Hazo-B’ carries ten 20-place liferafts and can tow those whon filled.
>■ Mi-14PLs carry four crow: two pilots, a night engineer and a systems operator.
profile
    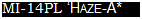
Equipped willi ;i search radar, dipping sonar, dispensers for sonolniovs aild tl. irvs and a tewed magnetic jorinulv detector (MAD), the origin. il anti-submarine version of die Haze’ was the Mi l lI’L. The Mi-l iPLM is a later variant with an improved engine and lias the search radar moved to the hotdwn rear end ol the fuselage For minesweeping. the МИ iin lla/e-B’ has a mine – adivatlng sleil m place of the MAO lowed behind the helicopter, il carries either
electrical cables r>i noise generators ti> detonate magnetl. or acoustic mines Л searchlight on the tailboom enables the sled to Ik* launched and recovered ai night. The It I variant was used by the foniter East German navy as well as the Soviet naval air arm. altliougli only about is were ініііі T he l. ultwaffe did not keep the East German navy’s six Mi-1 dll’s after reunification. Some have been converted to water bombers for use in civilian fire figliling o|H5iations.
MM4PL ‘Haze-A*
Type: land-based anti-submanne hotcopter
Powerplanl: two 1434-RW (1.925-hp) Klimov (Isoiov) TV3-117MT turboshatts
Max speed: 230 kmfti (143 m p. h.) at sea level
Climb rate: 468 nVmm (1.535 f. p.m I at sea level
Endurance: 5 hours 55 mm
Range: It 35 Km (704 ml.) with maximum fuel
Weights: empty 8902 kg <19.584 lb£ loaded 13000 kg (28,600 so,); maximum take-off 14000 kg (30.800 lb.)
Armament: torpedoes and depth charges as well as sonobuoys.’smoke.’?lare floats
Dimensions:
mam rotor diameter 21.29 m (69 ft 10 in ) length 18.37 m (60 It. 3 in,)
height 9.63 m (31 ft 7 in.)
rotor disc area 362 m’ (3.895 sq, ft I
COMBAT DATA

 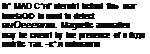 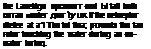 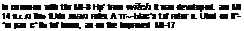 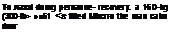         MAXIMUM SPEED MAXIMUM SPEED
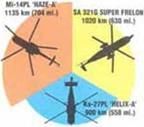
AwcraП ike tho Mi-14 wore not mter»Jod to bi txgh-Bpe«d mocNnan rjnjo and mdurarce w*m more important factor* AJ trvee types ere «paw* of *рем>» n tho 2S0 Knvh П50 m. phl band
МИ4П НАЛ-A" 230 tti’h. S—
(Ш M ».k |
|
Xi-2?n HUIX-A’ 250 «nvh (155 m. p.B.)
|
ENDURANCE
!»<• tareHJOMd M-14 fun »» (ям «nduanoo of »we «epmentettai!)p*v ‘H«4U’ is з «тилу comer-baiet) madvio, iwuJ ihu Supo> fmton tun, siroo ongme* and я Higher fuel ооплтлсп
   МІ-14Л НАЛА’ 5 tour* 55 nln МІ-14Л НАЛА’ 5 tour* 55 nln
The endurance of MOh type » «fkKWO
Dy the гяпцв »фіп»
Пі» vttluo* quoted ore »Of terry reoo* xifn a nannurn fuel ЮМ and ro weapons or other equipment on poor] Rang* імПслпаnee n parttCuUrty important lor cnmer-ISMed nrcrafl

Mil
• Assault transport • Civil helicopter • Gunship
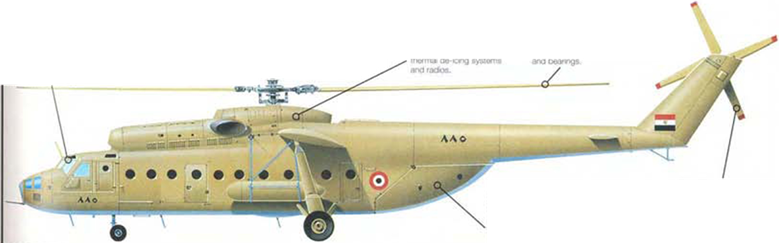
tough and resilient combat veteran, the Mil Mi-8 ‘Hip’, and the closely related Mi-17, stands tall in its reputation as one of the most versatile helicopters in the world. The Mi-8 is the most widely used helicopter in service, and is cheap to run, easy to maintain and powerful. The ‘Hip’ is primarily a troop carrier and civil transport. Other roles include helicopter gunship, airborne command post, search and rescue and oven communications jamming.
A Santa’s sleigh
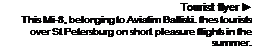   Even Santa Claus used the Mi-8 when travelling in distant areas of the Soviet Union. The Mi-8 was also vital to the Soviet oil industry, which explored in very remote areas. Even Santa Claus used the Mi-8 when travelling in distant areas of the Soviet Union. The Mi-8 was also vital to the Soviet oil industry, which explored in very remote areas.
  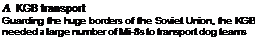 ▼ Assault transport ▼ Assault transport
This Mi-8 of the Indian air force is landing troops close to the front. Soviet Mi-8s made thousands of air assaults in Afghanistan, and large numbers wore shot down.
FACTS AND FIGURES

► More than 10,000 Mi-8s ond Ml-17s have been built, with many hundreds being exportod to more than 40 operators.
► The Mil MI-17 Is basically a Mi-8 with того power and a now tail rotor.
► The rare МІ-8РРА is a special communications jammer variant
► The MI-8 has fought in Afghanistan, Angola, Chechnya, Egypt. Mozambique and Nicaragua.
► Tho Czoch Republic, Hungary and Russia use the ‘Hip-G* command post version.
► The Mil Mi-14 ‘Haze’ anti-submarine helicopter is derived from the Mi-8.
 |
|
МІ-8Т Hip-C’
Type: assault transport helicopter
Powerplant: two i tiW-kW p.480rhp.) Ktmov (Isotov) TV-2-117A turboshaft engines
Mai speed: 250 knVh (155 m p. h.) at sea lovoi Typical cruising speed: 208 hm/h(130mpnt Radius of action: 350 km <217 ml.)
Ferry range: 930 km (575 mt і Service ceiling: 4500 m (15.000 ft)
Weights: tyjxcal empty 7160 kg (15.752 lb ); loaded 12000 kg (28.400 lb)
Accommodation: up to 28 combat troops in a cnlxn area behind pilots: combinations of rockets or 250-kg (650-lb) bomb» or UV-1G-57 rocket pods (16 x 57-mm projectiles each) 3stnde the fusetago
Dimensions:
main rotor diameter 21.29 m (69 ft. 10 in.) Sength 26.24 m (82 It. 9 in.)
horght 5.65 m (18 ft. 6 in.)
|
|
|
Tho Mi-8 was cheap enough to produce in thousands, giving tho Rod Army mass airlift capability.
|
|
|
The Ml-8 has a trad it tonal rotor hood wdt tiopong hinges a»d boar ngn Tho «nprovod f. tnr-tum rotcr tv«ad Of the Mi-17 needs
|
|
|
mnJntoramco and a mow txArt
|
|
|
The ispiov TV-2 rngre* ot tno V* 8 on very siritaf to nv» TV-3 групуй в the M -24 end
MM……….. TV-3 proven mom ruvitfu und
ecorvvh. .-it and drnmaticaty improved porter nvirvce in ‘hot-ond ftigh’ corvltcos
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
T)-jkcai top kpeedn for tna type and Aire of heocoptor i«vt to oc around 250 Mn.1i (155 mp. h J. The Puma had а тафті edge in в» respect wrtii a batter power-to-v.*ght ratio.
|
|
|
Loaarvj a Mi 8 в iwv thunk* to tho cfam*M doors at tho roar wt»ch con accommodate woe cargoes iirxl allow intartry so c*it very swiftly в an assadt
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
I*® "HIP-A’i The first.’Л-Й was the sngle – M»-8 ‘HIP-C: Wtti hvo engrros and the Sr1*** ntowype that tacked power and mar rotor blades, ttxi Mr 8 ‘Hp-C became j “uMafrAff-btadedmainrclor tho main assaut («.-tooptcr of live USSH
|
|
|
AWACS HP; It» Mi-17 was wen oervertod to act as <rt airborne eerty wvning and a»4tii mode» v.-tn sdfrrrwrafxl mchr amts
|
|
|
Mi-17 ‘HtP-H’: The Mi-17 teaued new mgres. geivbox and rater sbert ard was a W more powati and economical san the ».va
|
|
|
Mr8 ‘H1P-C: РгаЬэЫу tho most heostfy armed hefcoepter n service, tho ‘Hp-E’ carried up to s« pods erf 32 rackets.
|
|
|
|
    
Mil
 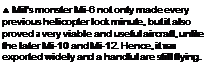  Sotting a trend for enormous gas turbine helicopters with massive load-carrying capability, the Soviet Union introduced the Mi-6 as a combined military/civil project in 1954. Intended primarily as a support vehicle for the air force’s huge An-12 transport, the Mi-6 needed just two ‘lifts’ to equal the payload of the transport. Most Mi-6s were grounded in 1992, after a long service including wartime operations in Afghanistan and Africa. Sotting a trend for enormous gas turbine helicopters with massive load-carrying capability, the Soviet Union introduced the Mi-6 as a combined military/civil project in 1954. Intended primarily as a support vehicle for the air force’s huge An-12 transport, the Mi-6 needed just two ‘lifts’ to equal the payload of the transport. Most Mi-6s were grounded in 1992, after a long service including wartime operations in Afghanistan and Africa.
|
A Siberian giant
Transporting massive piecet of machinery for the oil industry was a common fasJ. for the Mi-6 in the 1960s.
|
|
|
A Long service
About 800 Mi-6s were built between 1957 and 1980. During the aircraft’s busy life it fernod millions of passengers around the remotest regions of the USSR.
|
|
|
Troop truck ►
With extra seating the Mi-6 could carry up to 90 troops, but it was rarely used in a tactical role as size made it vulnerable.
|
|

 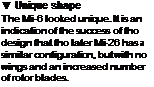
A Spacecraft recovery
Only tho Mi-6 was big enough to carry the crow capsule from the Vostok space launchers. The winf was mounted at 15 to the fuselage and provided about 20 per cent of the lift when cruising. The wings could be removed for the ‘flying crane’ role
► In 1961 the Mi-6 lifted height of 2738 motros and flew at 340.15 km/h over a 100-km circuit.
► Tho МІ-6Р was a firefighting version with a water tank, but it did not have stub wings.
>■ By 1990 Aeroflot Mi-6s had carried
15 million tonnes and 12 million people.
Bulgaria. Egypt. Ethiopia. Iraq, Libya. Peru, Syria and Vietnam.
>• Tho Mi-6R was a radio command post containing eight tonnes of equipment
► The Mi-6’s main rotor revolved clockwise at 120 rpm.
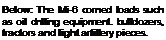     
During the 1950s tlic
Soviets lud industrial and military projects scattered aero" the country and tlte audit ■’•lies faced huge problems in supplying them. It was Гін this reason that a fleet of large transport helicopters Ikeeame пе<е»аіл Tlte Mi-6 met tlte requirement from І95Я.
Everything about tin* Mi-6 was large. Its engines were ;i giant leap in gas turbine technology as applied to heavyiili thing crane Itclkopters It pkniceied the use of supplementary wings lot added lift and achieved an incredible performance for a
madtme m its weight class, basically a freight carrier, military versions dominated the soo-plas production nm whidl ended in 198І To cope with adverse weather conditions the Mi-6 had its own rutorblade de-icing system and an auxiliary power unit. Tile aircraft was known as Shestyorka’ Clinic six ) by its crews Variants included firelighters. military jammers, civil hell-liners and medevac aircraft Military versions carried a machine – gun m tire nose
first flown in 1960. lire Mi-10 was a developed flying irane’
Above: Although later Mils like the Mi-26 could lift more, they wero not built in such largo numbers as the versatile Mi-6.
version of the Mi-6, including the engines, gear I tuxes and. stretched linden’.image. Not only was the Mi 6 the biggest helicopter in the world, it was also the fastest and hail outstanding range.
|
For иииіг ІПпу capacity nothing could match an NML
the ftotodyno also ruled on wings, whrch United «» carrying
capacity when taking ott the CM-47 hed a smerer mtarml volume
|
|
 |
|
The massve gearbox we*jhed no «ess than 3200 kg (7.040 ibj tl also Drove rwo 90–,VA alternators to esed the hoovy tood a* electro
|
|
|
the nve-uad&d main rotor was tnused on an extruded steel man spar wrth acrewed-cn зетовом sections of Ou’atumn. The btactes were etectro – ячтчіїу de iced, and were connected to the need by conventional hngoe
|
|
|
for 1 nurcoohv the Mi G had an urpnootiMwl oqupmont fit, nckxtng an autoert. ». Tho tght dock nod іеПоопіЮо Ooorr on ener sue lor the ptots and fight erg – – ■ A navgator sal n the gbeto rv. ,i«xt a radio coeratcr was ;*omeln».-) гагівях
|
|
|
CM-47 CHINOOK 8JC0 kg (11.8И f*.|
|
|
 |
|
Tho tail rotor woo л lour W. xkxt AV-бЗП typo wni a СиоЫ spar. v4l a BafcrSrto pfy outer, Cady versons had electro-thermal de-iong. when wm replaced by alcohol n tit or modolN
|
|
|
Large Ckynshuli doors made kxtdog and i/Ociatfing very easy The mam hold was 12 metres <39 ft) tong, hod о votime of 80 m – |Gt cu. yds l and nctoded its own etectrto wndi
|
|
|
®’9 lifters in the West
■ Atn – JPATIALE SA 321F: Пиз cfvil var. vrt •= >у Fmton. ore SA 321 tn no tong,* я ^1-mary version в still usod by Franco
|
|
 |
|
■ SIKORSKY CH-53: Still tho biggest rotary machine bu*U in tho West, the CH-53 was a groat success and is still m service. n Germany.
|
|
|
■ SIKORSKY S-64: The vYosl r, amvsw to tho MI-10, the Skycrane was usod oxtonaively in Vietnam to recover stiot-down UH-i«.
|
|
|
■ WESTLAND WESTMINSTER: Onty two Ot those aircraft wore ever built. It was canceled in favour of the larger Fairey Rotodyne
|
|
|
MI C M00K’ dOQlMtl |1M IT p. h I
CM-47 CHINOC* ?9t km* (18S n p. h.| VU
|
|
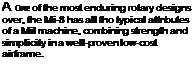  Mil Mil
| |
 The Mil Mi-26 brings size and brute
The Mil Mi-26 brings size and brute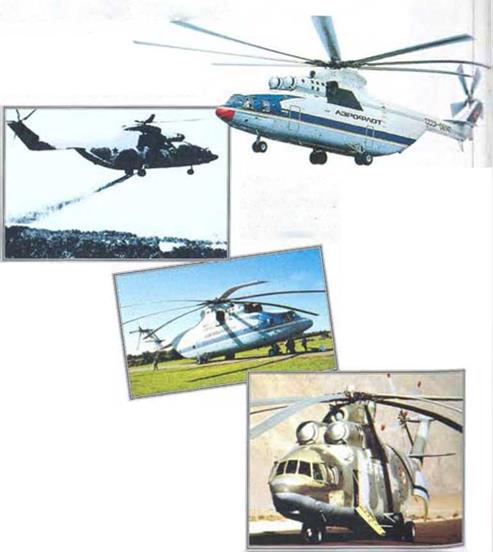 A Western visitor
A Western visitor With such a huge cargo hold, tho ‘Halo’ can carry a wide variety of loads. Its maximum payload is 20 tons, and it can carry light armoured vehicles, oilfield equipment or more than 100 passengers.
With such a huge cargo hold, tho ‘Halo’ can carry a wide variety of loads. Its maximum payload is 20 tons, and it can carry light armoured vehicles, oilfield equipment or more than 100 passengers. ◄ Crewing the giant
◄ Crewing the giant











 [
[ The presence of thoso troops and a single jeep lend scale to the sue of tho Mr-26. The fuselage is as largo as that of a C-130 Hercules and can accomodate up to 80 fully – equipped soldiers.
The presence of thoso troops and a single jeep lend scale to the sue of tho Mr-26. The fuselage is as largo as that of a C-130 Hercules and can accomodate up to 80 fully – equipped soldiers.
 ▼ Special requirement
▼ Special requirement
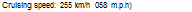

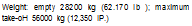

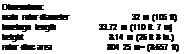











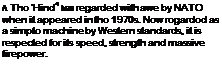
 Tho Mil Mi-24 ‘Hind’ is the hammor of the Russian army. A veteran of battles in Afghanistan and Angola, and most recently in Chechnya, the Mi-24 is a flying armoured personnel carrier, able to deliver a squad of soldiers and cover them with suppressive fire. Armed with a cannon and powerful laser-guided anti-armour missiles, and now fitted with the latest avionics and new engines, the ‘Hind’ is a highly potont attack
Tho Mil Mi-24 ‘Hind’ is the hammor of the Russian army. A veteran of battles in Afghanistan and Angola, and most recently in Chechnya, the Mi-24 is a flying armoured personnel carrier, able to deliver a squad of soldiers and cover them with suppressive fire. Armed with a cannon and powerful laser-guided anti-armour missiles, and now fitted with the latest avionics and new engines, the ‘Hind’ is a highly potont attack 
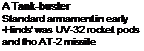


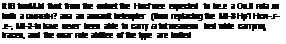
 td m Ы pUV. r giving, the cockpit of the had throe ranis The crew сопел! nd of * yanuxs n the centre tart я ftght fco pilot befxnd hen to the nw. end the let to the left rear, next to the co-priot In я rose a 12 7 mm І ЬО-cal I macrene – i luted in a tVmtXo mounting
td m Ы pUV. r giving, the cockpit of the had throe ranis The crew сопел! nd of * yanuxs n the centre tart я ftght fco pilot befxnd hen to the nw. end the let to the left rear, next to the co-priot In я rose a 12 7 mm І ЬО-cal I macrene – i luted in a tVmtXo mounting

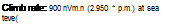
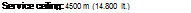
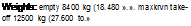
 Armament: one 12.7-mm machine-gun and lour AT-2 ‘Swatter’ anti-tank maples plus bombs or two rocket pods
Armament: one 12.7-mm machine-gun and lour AT-2 ‘Swatter’ anti-tank maples plus bombs or two rocket pods

 X» k«t (201 ■#.*.)
X» k«t (201 ■#.*.)


 Everything about the V-12 was enormous. The twin-rotor giant shattered every record for helicopter payload, and mado every previous rotarywing machine seem like a toy. But the problems of operating such a machine were also enormous and, despito the Ingenuity of the design, it was not roally a viablo machine for commercial use. After a momorable appearance at the Paris Air Show, the V-12 rarely flew again.
Everything about the V-12 was enormous. The twin-rotor giant shattered every record for helicopter payload, and mado every previous rotarywing machine seem like a toy. But the problems of operating such a machine were also enormous and, despito the Ingenuity of the design, it was not roally a viablo machine for commercial use. After a momorable appearance at the Paris Air Show, the V-12 rarely flew again.
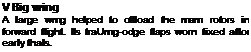



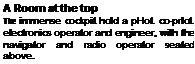 ▼ Paris performance
▼ Paris performance





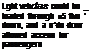
 The V-12 had а тпжигмп UAe-oft woght tX 105 torrw*. or mom than a MadM VUcim Bens** The CM-53 s dnirlod try №• much lug»
The V-12 had а тпжигмп UAe-oft woght tX 105 torrw*. or mom than a MadM VUcim Bens** The CM-53 s dnirlod try №• much lug»

 >.U httec&Ti, Out a an почти таеЫ-е. the M.-2S л emost as heavy as a My loaded С-1 Э0 Horses* at та»rm»n oi-up weghc.
>.U httec&Ti, Out a an почти таеЫ-е. the M.-2S л emost as heavy as a My loaded С-1 Э0 Horses* at та»rm»n oi-up weghc.
 Based on the Mi-8 ‘Hip’, the Mi-14 was developed as a land-based anti-submarine helicopter in the oarly-1970s. A boat hull and retractable landing gear were used to mako it suitable for amphibious operations, with more powerful engines compensating for tho additional weight. Flight tests started in September 1969. Specialised versions for minesweeping and search and rescue operations have also been produced.
Based on the Mi-8 ‘Hip’, the Mi-14 was developed as a land-based anti-submarine helicopter in the oarly-1970s. A boat hull and retractable landing gear were used to mako it suitable for amphibious operations, with more powerful engines compensating for tho additional weight. Flight tests started in September 1969. Specialised versions for minesweeping and search and rescue operations have also been produced.
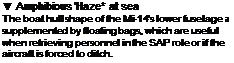








 MAXIMUM SPEED
MAXIMUM SPEED МІ-14Л НАЛА’ 5 tour* 55 nln
МІ-14Л НАЛА’ 5 tour* 55 nln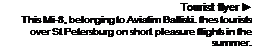
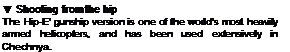
 Even Santa Claus used the Mi-8 when travelling in distant areas of the Soviet Union. The Mi-8 was also vital to the Soviet oil industry, which explored in very remote areas.
Even Santa Claus used the Mi-8 when travelling in distant areas of the Soviet Union. The Mi-8 was also vital to the Soviet oil industry, which explored in very remote areas.
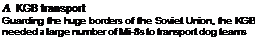 ▼ Assault transport
▼ Assault transport

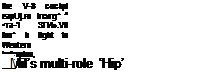





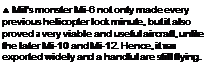
 Sotting a trend for enormous gas turbine helicopters with massive load-carrying capability, the Soviet Union introduced the Mi-6 as a combined military/civil project in 1954. Intended primarily as a support vehicle for the air force’s huge An-12 transport, the Mi-6 needed just two ‘lifts’ to equal the payload of the transport. Most Mi-6s were grounded in 1992, after a long service including wartime operations in Afghanistan and Africa.
Sotting a trend for enormous gas turbine helicopters with massive load-carrying capability, the Soviet Union introduced the Mi-6 as a combined military/civil project in 1954. Intended primarily as a support vehicle for the air force’s huge An-12 transport, the Mi-6 needed just two ‘lifts’ to equal the payload of the transport. Most Mi-6s were grounded in 1992, after a long service including wartime operations in Afghanistan and Africa.








 Mil
Mil