Mass, momentum, energy fluxes
The mass flux is the local mass flow rate per unit area moving through the control volume’s surface, shown in Figure 1.3. It is equal to the density times the surface-normal component of the velocity.
(mass flux) = pV ■ n
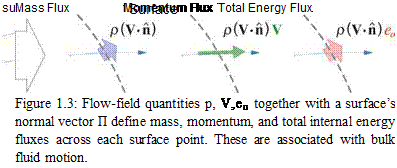 |
The mass flux also results in a momentum flux, defined as
momentum flux = (mass flux) x momentum/mass
= p(V ■ n) V
and which is a vector quantity. In an analogous manner, we can define the total internal energy flux,
total internal energy flux = (mass flux) x (total internal energy) /mass
= p(V ■ П) e0
where eo is the specific total energy, defined as the specific static energy plus the specific kinetic energy.
|
eo |
= e + V2 |
(1.17) |
|
V 2 |
= V ■V = u2 + v2 + w2 |
|
|
The specific total enthalpy ho and its flux are |
defined the same way. |
|
|
ho |
= h + V2 |
(1.18) |
|
total enthalpy flux |
= p(V ■ n) ho |













