Special Cases of Joukowski Airfoils
1.8.1 The Ellipse at Zero Incidence
Consider the circle centered at the origin and of radius b > a in the cylinder plane. Its image in the physical plane, through the Joukowski transformation, Eq. (2.39), is an ellipse centered at the origin, with main axis along Ox, from -2a to 2a and with parametric representation
![]() x = b~+a2 cos в = 2 cos в z = bl-a2 sin в = 2 sin в
x = b~+a2 cos в = 2 cos в z = bl-a2 sin в = 2 sin в
where в represents the polar angle in the cylinder plane. The ellipse has thickness e (small axis) and chord c (large axis). The potential function in the cylinder plane is
and the velocity components are
дФ b2 1 дФ b2
Vr = 17 = U 1 – 72 cosв, ув = r — = – U 1 + ^ sinв (2.63)
On the surface of the cylinder, this reduces to
Vr = 0, Ув = -2U sin в (2.64)
Using the chain rule
|
І |
дФ ___ дф dx і дф ді_
dr дx дг + дz дг
дФ _ дф д£ , дф 3z
дв = дx дв + дz дв
![]()
 |
|
|
|
|
|
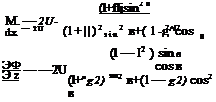 |
|
|
|
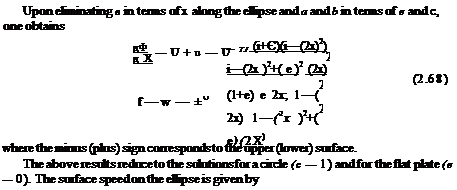 |
|
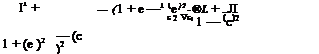 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
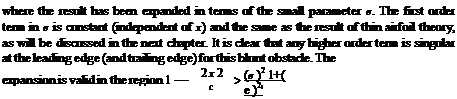 |











