Mesh Modification with Anisotropic Quality Measures
The mesh modification was applied to the DLR-F6 test case described in section 3.1.1 to see the influences on the aerodynamic coefficients. Again a target lift computation for CL = 0.5 was performed. After the flow computation the coarse, medium and fine mesh was modified by using a quality measure which uses an anisotropic metric. The metric was derived from the Hessian of the local Mach number. The flow was recomputed on the anisotropic mesh. This procedure was performed twice.
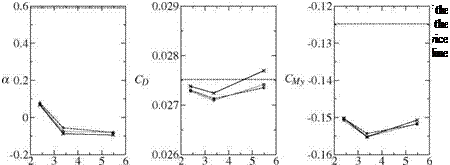
In figures 11(a)-(c) the angle of attack, the drag and the pitching moment are plotted as function of the grid points NP. The results computed on the base meshes are denoted by x. The results of the first and second mesh modification step is marked by о and □. The major improvements are observable for the drag on the coarse mesh, but the differences to the original mesh are relatively small in comparison to the changes caused by an adaptation with the new sensors. The major changes are observable in the resolution of the wake. In figure 12 the eddy viscosity is shown on four different meshes. The eddy viscosity on the coarse and fine base meshes (figure 12a,c) dissipates in the unstructured part very quickly, where on the anisotropically modified meshes (figure 12b,d) the wake is more resolved behind the wing, even on the coarse mesh. The improved wake resolution is observerable on the whole configuration.
In a second test the mesh modification with an anisotropic quality measure was applied to the TC-217 configuration (see section 3.1.2). For the test the mesh modification with the anisotropic quality measure was applied twice to the base mesh for а = «1. Again the metric was derived from the Hessian of the local Mach number. The results are presented in figure 13. The + and □ denote the results on the original and the modified mesh, respectively. Due to the mesh modification the lift decreases
by 8Cl « 8LC. The drag increases by SCd ~ 100DC. The result on the modified mesh increases the differences to the experimental results.











