THE L MATRIX IN TERMS OF ROTATION ANGLES
 |
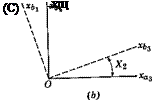 |
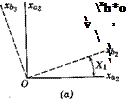
The transformations associated with single rotations about the three coordinate axes are now given. In each case Fa represents the initial frame, Fb the frame after rotation, and the notation for L identifies the axis and
Fie. 4.11 The three basic rotations, (a) About xai. (b) About хаґ (c) About xas.
the angle of the rotation (see Fig. 4.11). Thus in each case
![]() vb = Ьг(ХХ
vb = Ьг(ХХ
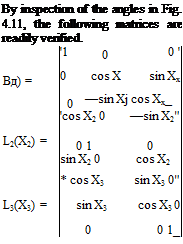 (4.5,2)
(4.5,2)
The transformation matrix for any sequence of rotations can be constructed readily from the above basic formulas. For the case of Euler angles, which rotate frame Fv into FB as defined in Sec. 4.3, the matrix corresponds to the sequence (X3, X2, Xj) = (ip, в, ф), giving
LBV = (ф) • Ь2(0) • L3(tp) (4.5,3)
[The sequence of angles in (4.5,3) is opposite to that of the rotations, since each transformation matrix premultiplies the vector arrived at in the previous step.] The result of multiplying the three matrices is
 |
cos oq, cos /3 —cos oq. sin fi —sin oq sin /3 cos $ 0
sin oq. cos /? —sin oq sin /3 cos oq











