Critical Flutter Velocity
In the present flutter analysis the elastic properties of blades are assumed uniform along the span and natural mode shapes are assumed same as those for the uniform fht plate. Vibration modes of the first and second bending orders with the natural frequencies шв і and шв a and the first and second torsion orders with the natural frequencies шт 1 and шт a are taken into account. The specified values are as follows; the mass ratio Mb/(np0b2arT (1 — h)) = 120, the normalized distance between the center of gravity and the elastic axis Xeg/ba = 0.141, the normalized radius of gyration re/ba = л/0Д the elastic axis position ze/Ca = —0.075, and the natural frequency ratios шт 1/шв 1 = 6.0, шв2/шв 1 = 6.3, шт2/шв 1 = 18.0. Here Mb is the mass of a blade, and ba = Ca/2.
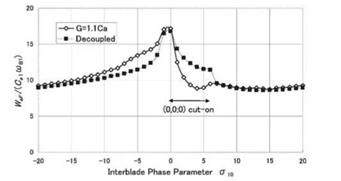
Figure 6 shows the dimensionless critical axial flow velocity at the flutter boundary dependent on interblade phase parameter а10 . The aerodynamic and geometrical conditions are same as those of case sub-sub in Table 2 except the blade row distance G = 1.1Ca. We can observe that the flitter velocity of
|
Figure 6. Critical axial fbw velocity for coupled bending-torsion flitter in case sub-sub |
the coupled blade rows is significantly lower than that of the decoupled blade row in the region where the duct mode (0, 0; 0) is cut-on.
2. Conclusions
(1) The effect of the neighboring blade row on the unsteady blade (loading is closely related to the state (cut-on, cut-off, near (resonance) of acoustic duct modes.
In the case of vibrating (subsonic cascade the supersonic neighbor cascade gives stronger (inflience on the unsteady aerodynamic work than the subsonic neighbor (cascade because of generation of a larger number of cut-on duct modes (due to interaction between cascades.
In the case of vibrating (supersonic cascade the aerodynamic work is significantly modified (around the resonance points of duct modes generated from aerodynamic (interaction with the neighboring cascade.
The critical flitter (condition can be significantly modified by the presence of the (neighboring cascade.
References