Concorde structure weight still "comparable" – 25 years later
The first example of technologies are weight improvements, listed m Table 2
|
OWE % |
PAY % |
QW£ PAY |
PAY №r |
l54>rOV*P!#r. t « |
Рапсе Mr. |
PAX No. |
MTOW Mo |
|
|
Concord# |
42.52 |
4.8 |
8.90 |
1.647 |
6.58 |
99 |
185.1 |
|
|
B737-200 M |
56.14 |
18.4 |
3.06 |
0,398 |
– – – |
4.07 |
107 |
52.6 |
|
B737-500 •> |
52.01 |
16,1 |
3.23 |
0.436 |
«9.55 |
4.48 |
108 |
60,6 |
|
B747-100 |
46.90 |
10.5 |
4.67 |
0.458 |
9.04 |
385 |
332.1 |
|
|
B747-400 |
45.99 |
9.61 |
4.79 |
0.345 |
24.67 |
13,27 |
420 |
394.6 |
|
АЭ40-300Е |
47,90 |
9,82 |
4.88 |
0.315 |
31.32 (ml. to |
13,24 |
295 |
271 |
|
……………… |
В747-Ю0) |
|
Table 2 Weight improvements since Concorde |
OWE operating empty weight. PAY payload. F: fuel
PAX: passengers HIOW maximum Ukr-oft weight
Part of improvement was used to mcreavr range, part Ю increase payload
Performance comparison by foe! per passenger kilometer
About the same development generation Concorde B737-200. B747*IOO
Modem aircraft. 25 yean later В737-500. B747-400. A340-300E
•’Data base for the different 87 37-versions seems to be і act* sister*. because the more efficient engine of the B737-300 (CFM-56 instead of JT-SD foe B737-200) should improve aircraft efficiency, at least for long ranges
Boeing В737-200 and B747-100 were developed in parallel wiih Concorde (40). The new generation of comparable size are B737-500. B747-400 and Airbus A340-300E |41); the latter being handicapped when compared with the B747-400. because it is a bit smaller Improvements of fuel per passenger-kilometers of more than 309r were achieved; but comparison to the old aircraft is difficult, because data base has changed (improved seating standards etc ).
When comparing Concorde’s structure weight, it is still comparable to the A340. (Comparison can only be made and was made by designing both aircraft with the same design tool. Assuming several structure technology standards, results showed the weights to reach the actual values of Concorde resp A340, when using the same structure standards for both designs (42)). But what arc the technologies leading to the subsonic weight improvement or Concorde’s advanced values?
• Because Concorde has only a small payload fraction, it is much more sensitive to weight increments; therefore more effort was spent for weight savings and expensive solutions became useful.
• Many (weight) improvements for transonic aircraft after B737-I00, B747-100 were provided by interdisciplinary effects like
high bypass engines or
optimized (nonlinear) transonic aerodynamics (Figure 10) via. increased wing profile thickness and volume, reduced wing sweep.
which cannot be transferred to a Concorde type configuration.
• System weight was only marginally reduced since Concorde.
• Since Concorde’s time many improvements in structure technology were not transferred into weight improsements. hut offset by advanced safety requirements; e g. new requirements for pressure losses, cabin evacuation or fire resistance of cabin equipment. But this is the world where a new SCT must fly.
|
transonic turbulent profit
conventional turbulent profit |
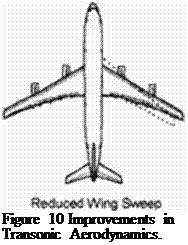 increased Wng Tmefcnaa* and Vc*jm«
increased Wng Tmefcnaa* and Vc*jm«












