General solution of Prandtl’s integral equation
This will be best understood if a particular value of в, or position along the span, be taken in Eqn (5.60). Take for example the position z = —0.5j, which is midway between the mid-span sections and the tip. From
z = —s cos 0, в = cos-1 j = 60°
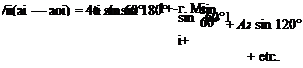 |
|
Then if the value of the parameter ^ is fi and the incidence from no lift is (c*i — aoi) Eqn (5.60) becomes
This is obviously an equation with A, A2, A3, A4, etc. as the only unknowns.
Other equations in which A, A2, A3, A4, etc., are the unknowns can be found by considering other points z along the span, bearing in mind that the value of fj, and of (a — ao) may also change from point to point. If it is desired to use, say, four terms in the series, an equation of the above form must be obtained at each of four values of в, noting that normally the values в = 0 and 7Г, i. e. the wing-tips, lead to the trivial
equation 0 = 0 and are, therefore, useless for the present purpose. Generally four coefficients are sufficient in the symmetrical case to produce a spanwise distribution that is insignificantly altered by the addition of further terms. In the case of symmetric flight the coefficients would be Ai, A3, As, At, since the even harmonics do not appear. Also the arithmetic need only be concerned with values of в between 0 and 7t/2 since the curve is symmetrical about the mid-span section.
If the spanwise distribution is irregular, more harmonics are necessary in the series to describe it adequately, and more coefficients must be found from the integral equation. This becomes quite a tedious and lengthy operation by ‘hand’, but being a simple mathematical procedure the simultaneous equations can be easily programmed for a computer.
The aerofoil parameters are contained in the expression
chord x two-dimensional lift slope
11 =———– ^——- :—————–
8 x semi-span
and the absolute incidence (a — ao). fi clearly allows for any spanwise variation in the chord, i. e. change in plan shape, or in the two-dimensional slope of the aerofoil profile, i. e. change in aerofoil section, a is the local geometric incidence and will vary if there is any geometric twist present on the wing. oo, the zero-lift incidence, may vary if there is any aerodynamic twist present, i. e. if the aerofoil section is changing along the span.
|
Example 5.3 Consider a tapered aerofoil. For completeness in the example every parameter is allowed to vary in a linear fashion from mid-span to the wing-tips. Mid-span data Wing-tip data
Total span of wing is 12.192m |
Obtain the aerofoil characteristics of the wing, the spanwise distribution of circulation, comparing it with the equivalent elliptic distribution for the wing flying straight and level at 89.4ms-1 at low altitude.
From the data:
Wing area 5 = 3£58 +L5!4 x 12.192 = 27.85m2
Aspect ratio (AR) = = 5.333
* 4 ‘ area 27.85
![General solution of Prandtl's integral equation Подпись: chord c = 3.048 1 J.vto — l . 3.048 (m.~« ' 5.5 — 5.8 /z [1+ 5.5 fc)J a° = 5.5 1 -^0]](/img/3130/image801_2.gif)
![]()
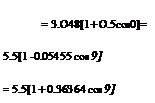 ©
©
|
Table 5.1
|
This gives at any section:
Cd
ц = —- = 0.34375(1 +0.5 cos 0)(1 -0.05455cos 0)
o S
and
fia = 0.032995(1 + O.5cos0)(l – 0.054 55 cos0)(1 + 0.363 64cos0)
where a is now in radians. For convenience Eqn (5.60) is rearranged to:
fia sin б = Asin0(sin0 + ц) + A3 sin30(sin0 + 3/i) + A5sin50(sin0 + 5/л)
+ A7 sin 70(sin 0 + 1ц)
and since the distribution is symmetrical the odd coefficients only will appear. Four coefficients will be evaluated and because of symmetry it is only necessary to take values of 0 between 0 and 7г/2, i. e. тг/8, 7t/4, 37t/8, 7t/2.
Table 5.1 gives values of sin0, sin лб, and cos 0 for the above angles and these substituted in the rearranged Eqn (5.60) lead to the following four simultaneous equations in the unknown coefficients.
0.0047 39 = 0.22079 A1 +0.89202 A3 + 1.25100 A5 +0.666 88 A7
0.011637 =0.663 19 Ai +0.98957 A3 – 1.315 95 A5 – 1.642 34 A7
0.021665 = 1.11573 A,. -0.679 35 A3 -0.896 54 Л5 + 2.68878 A7
0.032998 = 1.343 75 A -2.03125 A3 – 2.718 75 A5 – 3.40625 A7
These equations when solved give
А і = 0.020 329,Л3 = -0.000955, As = 0.001 029, A7 = -0.0002766
Thus
Г = 4sF{0.020 329 sin в – 0.000 955 sin 30 + 0.001029 sin 50 – 0.000 2766 sin 70} and substituting the values of 0 taken above, the circulation takes the values of:
|
0 |
0 |
тг/8 |
7t/4 |
Зтг/8 |
7t/2 |
|
zls і |
1 |
0.924 |
0.707 |
0.383 |
0 |
|
Tm2s |
0 |
16.85 |
28.7 |
40.2 |
49.2 |
|
Г/Го |
0 |
0.343 |
0.383 |
0.82 |
1.0 |
![]()
|
|
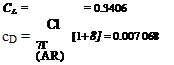 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
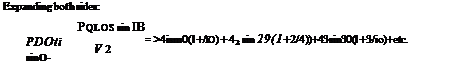 |
|
jUo«i sin# = A( + po)sb#
= Aj[ +2/Uo)sin20 0 = Ai(l + 3/Uo) sin3# etc.
Thus the spanwise distribution for this case is
Г = 4sV[Ai sin в + Ai sin 29]
|
(—Л*___ ^ 2(1 +2 к)) |
and the coefficients are











