Momentum Theory
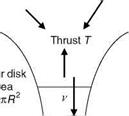
The momentum theory follows the basic laws of conservation of mass, momentum, and energy [9,10]. The action of the air on the rotor blades produces a reaction of the rotor on the air, which manifests in the form of thrust at the rotor disk. It is assumed that the rotor disk is composed of infinite number of blades, i. e., the rotor is considered to be an ‘‘actuator’’ disk. It is also assumed that the air is incompressible and frictionless and no rotational energy is imparted to the flow outside the slipstream. Velocity in the slipstream increases from zero at upstream infinity to v at the rotor disk and to w at downstream infinity (Figure 3.15). For air with density p and A the disk area, the law of conservation of mass gives
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
rn = pAv
![]() P<
P<
FIGURE 3.15 Flow across the actuator.
If T is the thrust at the rotor disk, it will be equal to the rate of change of momentum, i. e.,
T = m (w — 0)
= pAvw (3.37)
From the law of conservation of energy, we have
T v = 1 mw2 (3.38)
Substituting for T from the momentum conservation equation, we have
pAvwv = 2 pAvw2
or
v = 2 w (3.39)
Thus, the velocity at downstream infinity is twice the velocity at the rotor disk. From the momentum conservation equation, the relation between v and thrust T now becomes
T = pAv2v
or
The term “T/A” is also known as disk loading. The induced power for the rotor can be written as
![]()
![]() T
T
P = T v = TJ——–
V 2pA
In nondimensional form, thrust and power coefficients are given by
Here, V is the angular velocity and R is the radius of the rotor.
The inflow ratio l is given by
The hovering efficiency of the rotor is defined by figure of merit M, defined as
minumum power required to hover
actual power required to hover
The ideal value of M is equal to 1. However, for most rotors, the value lies between 0.75 and 0.8.











