Probes
A wire is stretched between two metal prongs, similar to sewing needles (Figure 3.3). The diameter of the wire is limited by the need to have an adequate electrical resistance, a very rapid response and a high resolution. The diameter normally employed is 5 pm. To increase the size of the
|
Breaking stress x 10-4 (Ncrrr2) |
Maximum temperature (°С) |
Soft- solderable |
Weldable |
Available as Wollaston wire |
Minimum diameter (pm) |
ІЇК1) |
Resistivity at 0°C x 106 fl(cm) |
Thermal conductivity at 0°C (Wcm_1K_1) |
|
|
Tungsten |
20 и – 25 |
300 (oxidizes) melting point 3382 |
No |
Yes if plated |
No |
2.5 4 3.8 |
0.0035 4 0.0047 |
4.9 4 5.5 |
1.9 |
|
Platinum |
2 и – 3.6 |
800 4-1200 melting point 1800 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
1.0 4 1.25 |
0.0030 4 0.0038 |
9.8 4 10 |
0.7 |
|
Platinum- iridium (80/20) |
7 |
750 |
Yes |
Yes |
38 |
0.00085 |
32 |
0.2 |
|
|
Platinum- rhodium (90/10) |
6 |
1400 melting point 1600 |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
0.6 |
0.0016 |
9 |
0.4 |
|
Table 3.1 |
|
Sensor materials for hot wire probes |
|
|
||
|
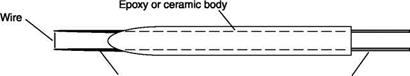
wires in order to make them more manageable during processing and assembly and/or improve the weldability, platinum wire covered with a thick coating of silver (Wollaston wire) or gold-plated tungsten wires are used. After the wire is welded to the supports, the plating is removed with an acid in the zone to be used as a sensor.
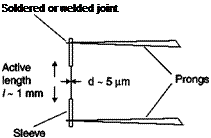
The length of the wire is limited by the need to have a good spatial resolution: the sensor simply senses an average speed on its length and the objective is to measure the speed at one point. The length must also be much smaller than the size of the vortices. Plated tungsten wires are used with the minimum length of 1.2 mm (miniature probes). These probes are best used in air flow with turbulence intensity less than 10% and have the highest frequency response; they can be repaired.
If the wire is too short, aerodynamic interference of the prongs has a not negligible effect and, due to the conduction towards the supports, the temperature of the wire is not uniform. These drawbacks can be alleviated using a longer wire (= 3 mm) of the Wollaston type or plated tungsten and using as a sensor only the central part of it (1 mm) after removing the plating with a chemical attack (Figure 3.4). These probes are used in air streams with intensities of turbulence up to 25% and have a frequency response less than that of miniature probes; they can be repaired.
![]()
 |
Gold-plated sensor
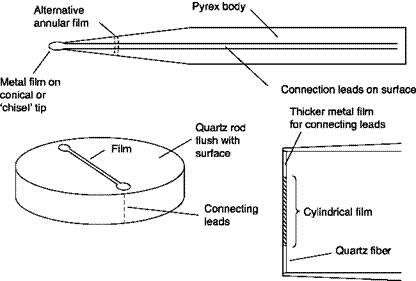 |
Another type of sensor, called fiber hot film, has replaced the wire in many heavy duty applications (air containing powder, liquid). This type of sensor is made with a quartz fiber on which a film of conductive material covered with quartz is deposited (Figure 3.5). The diameter in this case is the order of 70 pm, the frequency response is lower than that of the wires; they can be repaired.
In addition to the form of wire, hot film sensors can be realized in the most varied shapes: cone or wedge, cylinder, etc. (Figure 3.5). They can be used from low to moderate frequencies of fluctuation of speed; they cannot easily be repaired.
The films are usually made of platinum or nickel, the support is made of Pyrex glass or quartz fiber. If the fluid is a conductive liquid, the sensor must be electrically insulated from the liquid using a thick quartz coating.











