Wave Number Analysis of Extrapolation
It will be assumed that the function f(x), to be extrapolated, has a Fourier transform /(a). f(x) and /(a) are related by
TO
f (x) = J f (a) eiaxda. (11.9)
— TO
For convenience, let the absolute value and argument of f(a) be A and ф, respectively, i. e.,
A (a) = |/(a)| and ф(а) = arg[ f(a)]
so that Eq. (11.9) may be rewritten as
![]() f (x)=/ A(a)‘iax+t’n’d
f (x)=/ A(a)‘iax+t’n’d
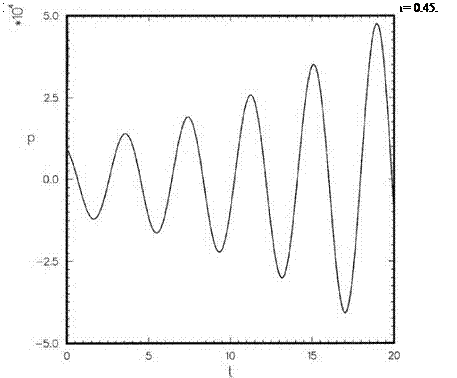
A simple interpretation of Eq. (11.10) is that f(x) is made up of a superposition of simple waves with wave number a and amplitude A (a). The primary goal here is to develop an extrapolation scheme that is highly accurate over the low wave number range, say, – к < a Ax < к. For this purpose, it will be sufficient to consider waves with unit amplitude over the desired band of wave numbers. The simple wave with wave number a to be considered is
![]()
f (x) = ei[ax+<p(a)]











