The DRA (RAE) research Puma, SA330
The SA 330 Puma is a twin-engine, medium-support helicopter in the 6-ton category, manufactured by Eurocopter France (ECF) (formerly Aerospatiale, formerly Sud Aviation), and in service with a number of civil operators and armed forces, including the Royal Air Force, to support battlefield operations. The DRA (RAE) research Puma XW241 (Fig. 4B.5) was one of the early development aircraft acquired by RAE in 1974 and extensively instrumented for flight dynamics and rotor aerodynamics research. With its original analogue data acquisition system, the Puma provided direct support during the 1970s to the development of new rotor aerofoils through the measurement of surface pressures on modified blade profiles. In

Fig. 4B.5 DRA research Puma XW241 in flight
|
Table 4B.3 Configuration data – Puma
|
the early 1980s a digital PCM system was installed in the aircraft and a research programme to support simulation model validation and handling qualities was initiated. Over the period between 1981 and 1988, more than 150 h of flight testing was carried out to gather basic flight mechanics data throughout the flight envelope of the aircraft (Ref. 4B.1). The aircraft was retired from RAE service in 1989.
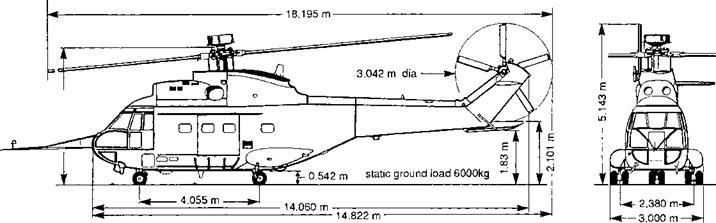
A three-view drawing of the aircraft in its experimental configuration is shown in Fig. 4B.6. The aircraft has a four-bladed articulated man rotor (modified NACA 0012 section, 3.8% flapping hinge offset). The physical characteristics of the aircraft used to construct the Helisim simulation model are provided in Table 4B.3.











