Lift, Pitching Moment, and the Center of Pressure Location for Circular Arc Aerofoil
We know that the lift L, pitching moment about the leading edge of the aerofoil Mle and the pressure p acting on the aerofoil can be expressed as:
1 2
L = – pU 2cCL
Mie = 2 pU 2c2Cmic p = pUk.
Now, substituting:
the pressure becomes:
Also,
x = — (1 — cos в).
Therefore, the lift becomes:
L = I pdx
П _
![]()
= — pU2c 2 І а(1 + cos в) + 2вsin2 в
that is:
The lift coefficient is:
![]() L
L
2 pU 2c
This gives:
Thus the lift-curve slope is:
From the above relations for CL and dCL /da, it is evident that:
at a = 0, CL = 2пв at a = —в, CL = 0
and the lift-curve slope is independent of camber.
For a cambered aerofoil, we have:
![]() 2л (a + в)
2л (a + в)
![]() dCL
dCL
ЮГ(a
For CL = 0, a = —в or —aL=0 = в. Thus:
The pitching moment is:
Mie = — pxdx
0
= —2pU2c2f (a + 2в).
Therefore, the pitching moment coefficient becomes:
In terms of CL, the CMle can be expressed as follows. By Equation (6.23a), we have the CL as:
Cl = 2n (a + в).
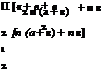 |
|
The expression for CMle, in Equation (6.25), can be arranged as:
But CL = 2п (a + в), thus:
![]() 1
1
Cm“ = —2
or
The center of pressure coefficient, kcp, becomes:
Thus, the effect of camber is to set back the center of pressure by an amount which decreases with increasing incidence or lift. At zero lift, the center of pressure is an infinite distance behind the aerofoil, which means that there is a moment on the aerofoil even when there is no resultant lift force.
Comparing this with Equation (6.17a) (CMle =— |a) for flat plate we see that the camber of circular arc decreases the moment about the leading edge by пв/2.
Example 6.3
(a) A flat plate is at an incidence of 2° in a flow; determine the center of pressure. (b) If a circular arc of 3% camber is in the flow at the same incidence, where will be center of pressure?
Solution
(a) Given, a = 2°.
For a flat plate, by Equation (6.16), the lift coefficient is:
CL = 2пa
= 2п x (2 x —— 2
V 180/
= 0.219.
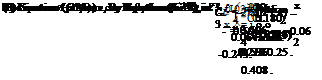 |
By Equation (6.17):
Aliter:
Note that the kcp is also given by Equation (6.27), as:
![]()
![]() 1 n в = 4 + 2CL 1 i n x 0.06 — 4 + 2 x 0.596 = 0.408.
1 n в = 4 + 2CL 1 i n x 0.06 — 4 + 2 x 0.596 = 0.408.
This is the same as that given by dividing CMle with CL.











