. Wing Geometric Parameters
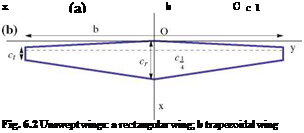
The wing planform geometry can be described with several parameters. Unswept
wings are shown in Fig. 6.2. The quarter chord c 1 is parallel to the у-axis. In the
4
case of the trapezoidal wing, the root chord, cr or c0, and the tip chord, ct, are two parameters that define the planform geometry.
 |
|
The quarter-chord sweep angle, Л c is another geometric parameter for swept wings such as the rectangular swept wing and the delta wing, Fig. 6.3.
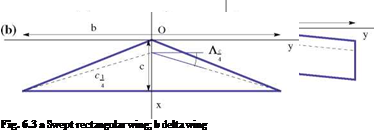 |
The delta wing is usually the preferred design for low aspect ratio supersonic aircraft wings.
One defines the mean aerodynamic chord as
The mean aerodynamic chord plays a role in the wing pitching moment.
When facing the wing and the fuselage, the angle of the wing with the horizontal plane is called the dihedral angle. The dihedral angle can be positive or negative, see Fig. 6.4. A positive dihedral angle introduces rolling stability, known as dihedral effect, but this and other unsymmetrical flow conditions such as yaw, are outside the scope of this book.
![]()
 (a)
(a)
 |
(b)











