Example – Sea King
 |
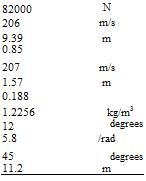 |
The following data are used:
This produces the graph in Figure 6.28.
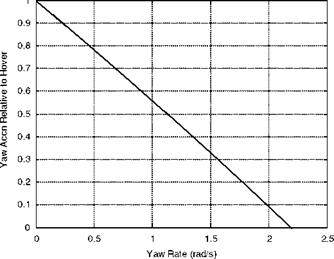
The figure shows the yaw acceleration attainable with the rotor on the point of stall. The yaw acceleration is normalized with the value in steady hover – that is, no yaw rate. Notice that, as the yaw rate increases, the thrust potential reduces as the precessional effects emerge by limiting the collective pitch which can be achieved before part of the tail rotor enters stall – in this case a yaw rate of 2.2rad/s.
|
Figure 6.28 Yaw acceleration limit due to precession caused by yaw rate |